Pruning is one of the most important tasks for maintaining healthy rose bushes. It can help rejuvenate your plants, promote better flowering, and ensure their longevity. Whether you’re an experienced gardener or a beginner, understanding the best time and method to prune different types of roses can make a world of difference in your garden’s beauty and productivity. This guide provides an in-depth look at the different types of roses and the proper techniques for pruning them to achieve vibrant, healthy blooms all year round.
Why Prune Roses?
Pruning serves several important purposes. For one, it helps remove dead, diseased, or damaged wood, which can harbor pests and diseases. It also promotes air circulation, which helps prevent fungal infections. Additionally, pruning encourages new growth, allowing roses to produce larger, more beautiful flowers. Regular pruning keeps your rose bushes from becoming too overgrown and helps shape them for a cleaner, more aesthetically pleasing appearance.
When Should You Prune Roses?
The timing of your pruning depends on the type of rose you are working with and your climate. Generally, roses should be pruned during the dormant season, which is in late winter to early spring, just before new growth starts. This is typically when forsythia flowers bloom, signaling it’s time to prune most rose varieties. However, the timing may vary slightly based on your location and the specific rose type.
How to Prune Different Types of Roses
Each type of rose bush requires a slightly different approach to pruning. Understanding these differences will help you give your roses the best possible care. Below, we break down the ideal pruning techniques for five of the most common types of roses: floribunda, shrub, climbing, wild, and hybrid tea roses.
1. Floribunda Roses
Floribunda roses are known for their clusters of small flowers and long blooming period. They are a hybrid between hybrid tea roses and polyantha roses. These roses benefit from regular pruning to remove old and weak growth, allowing for more vigorous new growth and increased flower production.
- When to Prune: Prune floribunda roses in early spring when the forsythia blooms, just before the new growth begins.
- What to Cut: Remove any old, weak, or diseased canes. Prune back the remaining stems to 3–5 buds to encourage new growth.
- Why Prune: This method helps maintain the bush’s shape and encourages healthy, abundant blooming.
2. Shrub Roses
Shrub roses are generally more resilient and hardy than other types of roses. They have a bushy, compact growth habit and often require less pruning than floribundas or hybrid teas. However, regular pruning is still necessary to keep them healthy and looking their best.
- When to Prune: Prune shrub roses in late winter or early spring, ideally when the weather is milder, and the threat of frost has passed.
- What to Cut: Remove any weak, damaged, or crossing branches. Leave the main stems intact and trim side shoots lightly.
- Why Prune: Pruning helps maintain a balanced shape, encourages new growth, and prevents overcrowding, which can lead to disease and pests.
3. Climbing Roses
Climbing roses add beauty and vertical interest to any garden. Unlike bush roses, climbing roses have long canes that need to be trained onto a support structure, such as a trellis, fence, or arch. Pruning climbing roses properly is essential for managing their growth and ensuring they bloom profusely.
- When to Prune: Prune climbing roses after they finish blooming, typically in late summer or early fall.
- What to Cut: Trim side shoots to 2–3 buds above a healthy outward-facing bud. Do not prune the main canes, as they will produce the majority of the flowers in the following season.
- Why Prune: Pruning climbing roses encourages lateral growth and helps maintain the desired shape of the vine. It also ensures that the plant produces flowers on new growth in the next bloom cycle.
4. Wild Roses
Wild roses are known for their natural beauty and ability to grow in a more untamed, sprawling manner. These roses are less demanding than hybrid varieties and tend to require minimal pruning. However, cutting back dead or damaged growth is still essential for keeping the plant healthy.
- When to Prune: Prune wild roses in late fall after blooming or early spring before new growth begins.
- What to Cut: Only remove dead or diseased branches, as these roses are best left to grow naturally. Avoid cutting back healthy growth, as wild roses benefit from their natural form.
- Why Prune: Pruning wild roses helps improve air circulation, reduces the risk of disease, and ensures the plant remains healthy without disrupting its natural growth habit.
5. Hybrid Tea Roses (Edelrosen)
Hybrid tea roses are perhaps the most well-known type of rose, prized for their large, elegant blooms. They require regular, careful pruning to maintain their shape and produce abundant flowers. Hybrid tea roses should be pruned in early spring to prepare for a new season of growth.
- When to Prune: Prune hybrid tea roses in early spring when new growth begins.
- What to Cut: Remove weak or dead canes and trim the main stems by about one-third. This encourages strong, healthy growth.
- Why Prune: Pruning hybrid tea roses promotes vigorous new growth and ensures that the plant directs its energy into producing large, beautiful flowers.
Basic Pruning Techniques
No matter which type of rose you are pruning, certain general pruning techniques apply. Here are some essential tips to ensure you get the best results:
1. Use Clean, Sharp Tools
Always use sharp, clean pruning shears, loppers, or saws to make precise cuts. This reduces the risk of damaging the plant and minimizes the chance of introducing diseases. Clean your tools before and after use to prevent cross-contamination between plants.
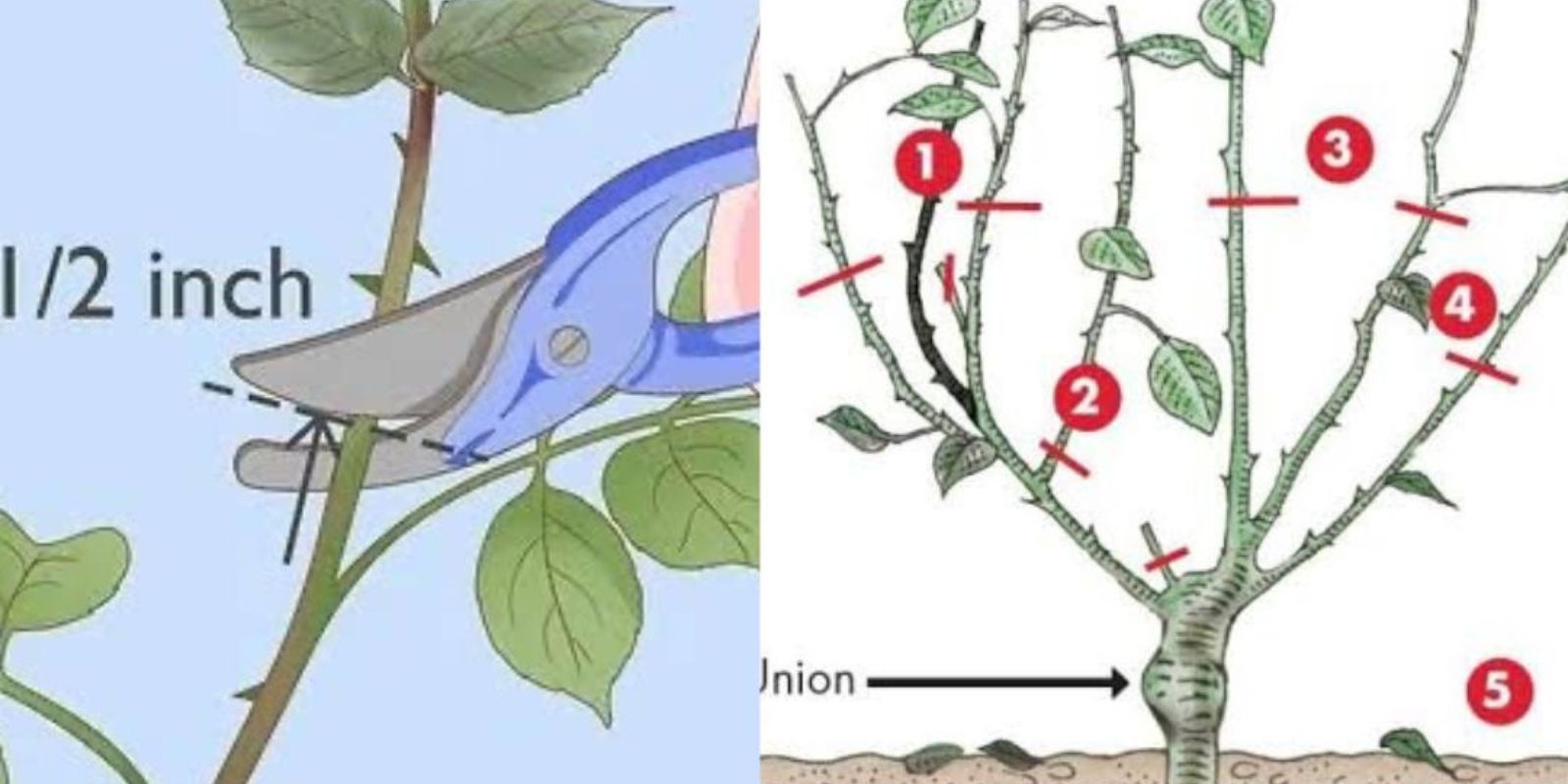
2. Cut Above an Outward-Facing Bud
When making cuts, always trim just above an outward-facing bud or branch. This encourages new growth to grow outward rather than inward, resulting in a more open, well-structured bush. It also allows better airflow, reducing the risk of fungal diseases.
3. Cut at a Slight Angle
Make cuts at a slight angle (about 45 degrees) to ensure water drains off the cut and doesn’t collect on the stem. This helps prevent rot and encourages healthy growth.
4. Remove Dead or Diseased Wood
Remove any wood that looks dead, diseased, or damaged. These branches will not contribute to the health of the plant and can serve as a breeding ground for pests and disease. Removing them helps improve air circulation within the bush and prevents the spread of problems.
5. Avoid Over-Pruning
While it’s important to prune your roses regularly, avoid over-pruning. Too much pruning can stunt the plant’s growth and reduce flower production. Be mindful of how much you cut away and make sure to leave enough healthy growth to support future blooms.
Conclusion: Pruning for a Thriving Rose Garden
Pruning your rose bushes is an essential part of their care. Whether you have floribunda, shrub, climbing, wild, or hybrid tea roses, proper pruning will help keep your plants healthy, beautiful, and productive. By following the recommended pruning times and techniques for each rose variety, you can enjoy an abundant display of blooms and a thriving garden season after season.
Remember, pruning is not just about cutting back; it’s about giving your roses the best possible chance to flourish. So grab your pruning shears, roll up your sleeves, and get started on creating a stunning rose garden today!
Happy gardening!