Grafting is an ancient horticultural practice that has been used for centuries to propagate and enhance fruit trees. It allows gardeners to combine the desirable traits of two different plants into one, resulting in healthier trees, improved fruit quality, and greater yields. This comprehensive guide will explore the fundamentals of grafting fruit trees, including techniques, best practices, and tips for success, all while emphasizing the benefits of this rewarding gardening skill.
Understanding Grafting
Grafting involves joining two plant parts: the scion (the upper part that produces the fruit) and the rootstock (the lower part that provides the root system). The two parts must be compatible, meaning they belong to the same species or genus. Successful grafting creates a union that allows nutrients and water to flow between the two, ultimately resulting in a thriving fruit tree.
Benefits of Grafting
- Disease Resistance: Grafting onto a disease-resistant rootstock can protect the tree from soil-borne diseases and pests.
- Improved Fruit Quality: By selecting a high-quality scion, gardeners can produce fruit with better flavor, texture, and size.
- Faster Fruit Production: Grafted trees often bear fruit sooner than those grown from seed, allowing for quicker harvests.
- Space Efficiency: Grafting can allow for multiple varieties of fruit to be grown on a single tree, maximizing space in a garden or orchard.
- Custom Varieties: Grafting allows gardeners to create unique combinations of fruit types that may not be available commercially.
Choosing the Right Time to Graft
Timing is crucial for successful grafting. The best time to graft fruit trees is during the late winter or early spring when trees are still dormant. This timing allows for a smoother healing process as the trees begin to grow after their dormant period. Avoid grafting during extreme temperatures or when the tree is under stress from drought or disease.
Selecting Healthy Scions and Rootstocks
The success of your grafting efforts hinges on the quality of the scion and rootstock. Here are some tips for selecting the best materials:
- Scion Selection:
- Choose a healthy, disease-free scion from a mature tree that produces the desired fruit variety.
- Look for scions with good vigor, a strong growth habit, and well-formed buds.
- Ideally, select scions that are pencil-sized in diameter.
- Rootstock Selection:
- Select a rootstock that is compatible with your chosen scion variety. Research compatibility within the same species or genus.
- Choose rootstocks known for their disease resistance, vigor, and growth habit.
- Consider the eventual size of the tree when selecting a rootstock; some will produce dwarf or semi-dwarf trees, while others will lead to standard-sized trees.
Preparing Your Tools
Before starting the grafting process, gather the necessary tools. Properly prepared tools can make a significant difference in the success of your grafting efforts. Here’s what you’ll need:
- Grafting Knife: A sharp knife specifically designed for grafting will help you make clean cuts.
- Pruning Shears: These will be used to cut away any branches or foliage from the scion and rootstock.
- Grafting Tape or Parafilm: These materials will be used to secure the graft and protect it from drying out.
- Optional Tools: A saw may be needed for larger rootstocks, and rubber bands can help secure the graft in certain techniques.
Make sure to clean your tools before use to prevent the spread of disease. Sanitizing with rubbing alcohol or a diluted bleach solution can help ensure your grafts have the best chance of success.
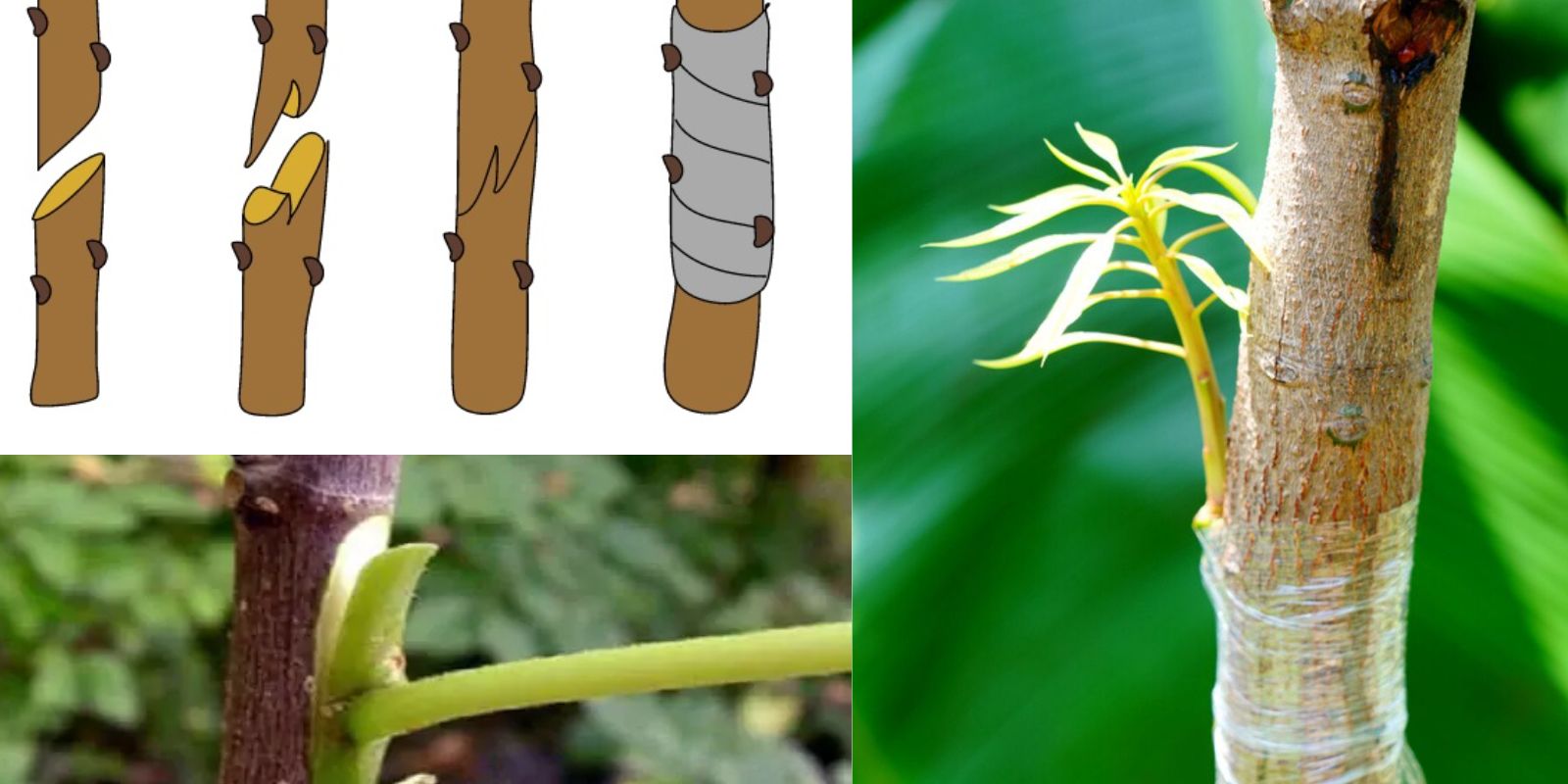
Grafting Techniques
There are several techniques for grafting, each suited for different situations and types of trees. The most common grafting methods include:
1. Whip-and-Tongue Grafting
- Description: This technique is particularly effective for grafting two stems of similar size.
- Steps:
- Make a diagonal cut on both the scion and rootstock, ensuring they match in size.
- Create a tongue by making a small vertical cut at the base of the diagonal cut on both parts.
- Fit the scion and rootstock together, aligning the cambium layers (the green tissue just beneath the bark).
- Secure the graft with grafting tape or parafilm.
2. Cleft Grafting
- Description: This method is ideal for grafting a smaller scion onto a larger rootstock.
- Steps:
- Make a straight cut down the center of the rootstock, about 2-3 inches deep.
- Create a wedge shape at the base of the scion by cutting diagonally on both sides.
- Insert the scion into the cleft of the rootstock.
- Wrap the graft tightly with grafting tape to hold it in place.
3. Bud Grafting (T-budding)
- Description: This technique is useful for grafting a single bud onto a rootstock.
- Steps:
- Make a T-shaped incision in the bark of the rootstock.
- Carefully remove a bud from the scion with a small piece of bark.
- Slide the bud into the T incision, making sure the cambium layers touch.
- Secure the graft with tape, leaving the bud exposed.
Securing the Graft
Once you’ve completed the grafting process, it’s crucial to secure the grafted area properly. Use grafting tape or parafilm to wrap the graft tightly, ensuring that moisture and debris do not enter. Be careful not to wrap too tightly, as this could restrict the growth of the scion.
Additionally, consider placing a plastic bag or a humidity dome over the graft to maintain moisture during the healing process. This can help prevent the scion from drying out.
Caring for the Grafted Tree
After grafting, it’s important to monitor and care for the tree as it heals. Here are some essential care tips:
- Watering: Ensure the tree receives adequate moisture during the healing process. Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged.
- Shade: If possible, provide shade for the grafted area during the hottest part of the day. This can help prevent stress and sunburn.
- Remove Suckers: If suckers (shoots) emerge from the rootstock below the graft, remove them promptly. These can divert energy from the scion and inhibit its growth.
- Monitor for Growth: Check the graft regularly for signs of growth. A successful graft will produce new leaves and buds in a few weeks.
- Patience: Grafting can take several weeks to months for the scion to successfully integrate with the rootstock. Be patient and allow the tree time to establish itself.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
While grafting can be highly rewarding, it is not without challenges. Here are some common issues that may arise during the grafting process and how to address them:
- Graft Failure: If the graft doesn’t take, check the alignment of the cambium layers. Misalignment can prevent nutrient flow. Try again with fresh materials.
- Dying Scion: If the scion wilts or dies, it may not have been healthy or compatible with the rootstock. Ensure both parts are healthy before grafting.
- Overheating: If the graft area is exposed to extreme heat, it can dry out. Consider providing shade or using a humidity dome to keep the area moist.
- Pests and Diseases: Monitor for signs of pests or diseases at the graft site. Remove any affected leaves or buds to prevent spread.
Conclusion
Grafting fruit trees is a rewarding skill that can enhance your gardening experience and yield a bountiful harvest. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can master the art of grafting and create healthier, more productive fruit trees in your garden. Whether you’re looking to improve disease resistance, achieve better fruit quality, or grow unique varieties, grafting is a technique that every gardener should consider. Start your grafting journey today, and enjoy the satisfaction of cultivating your very own fruit trees!
Call to Action
Ready to take your gardening skills to the next level? Gather your materials, choose your favorite fruit varieties, and start grafting today! Share your experiences and successes with fellow gardeners, and don’t hesitate to ask questions. Happy grafting! 🌳🍏