Having healthy soil is one of the most important steps toward maintaining a thriving garden. Knowing what nutrients your soil has or lacks, understanding its pH levels, and determining its structure can guide you in making the right choices to improve plant growth. You can easily test the quality of your soil at home using simple methods to check for pH, nutrients, drainage, and texture.
Why Test Your Soil?
Understanding the composition of your soil is crucial for ensuring that your plants get the nutrients they need. Different plants require different types of soil. For instance, some prefer acidic soil while others thrive in more alkaline environments. Conducting a soil test helps you tailor your amendments (fertilizers, compost, lime, etc.) to what your soil truly needs, which can lead to bigger blooms, better vegetable yields, and healthier plants overall.
Key Aspects of Soil Testing
- pH Level
Soil pH affects how nutrients are absorbed by plants. A balanced pH ensures that the soil’s nutrients are accessible to the plants. Most plants prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH range (around 6.0–7.0), but certain plants, like blueberries and azaleas, thrive in more acidic conditions. - Nutrient Content
Nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) are the three key nutrients essential for plant growth. If your soil lacks any of these nutrients, your plants might suffer from stunted growth, yellowing leaves, or poor flower production. - Soil Texture
Soil texture impacts water retention and root growth. Sandy soils drain quickly but may not hold nutrients well. Clay soils hold water and nutrients but can become compacted, making it hard for roots to grow. Loamy soil, which is a mix of sand, silt, and clay, is ideal for most plants because it retains moisture without becoming waterlogged. - Drainage
Poor drainage can suffocate plant roots, leading to root rot and other diseases. Testing your soil’s drainage will help you determine whether your plants are getting too much or too little water.
How to Test the Quality of Your Soil at Home
Now, let’s dive into the step-by-step process for testing your soil at home. These methods will help you assess your soil’s pH, drainage, nutrient content, and texture.
1. Collect Soil Samples
- Use a trowel to dig small soil samples from several areas of your garden. Aim for areas where you plan to plant, and dig about 6-8 inches deep to get a representative sample.
- Mix all the soil samples together in a clean container. This gives you an average sample to work with, reflecting the overall condition of your soil.
- Remove any rocks, sticks, or debris from the soil, and allow it to dry if it’s too wet.
2. Test Your Soil’s pH
You can test the pH of your soil using a home pH test kit or even simple household items:
Option 1: Using a pH Test Kit
- Purchase a soil pH test kit from a garden center.
- Follow the instructions on the kit by mixing soil with water and adding the provided solution or strip. Compare the resulting color to the pH scale provided.
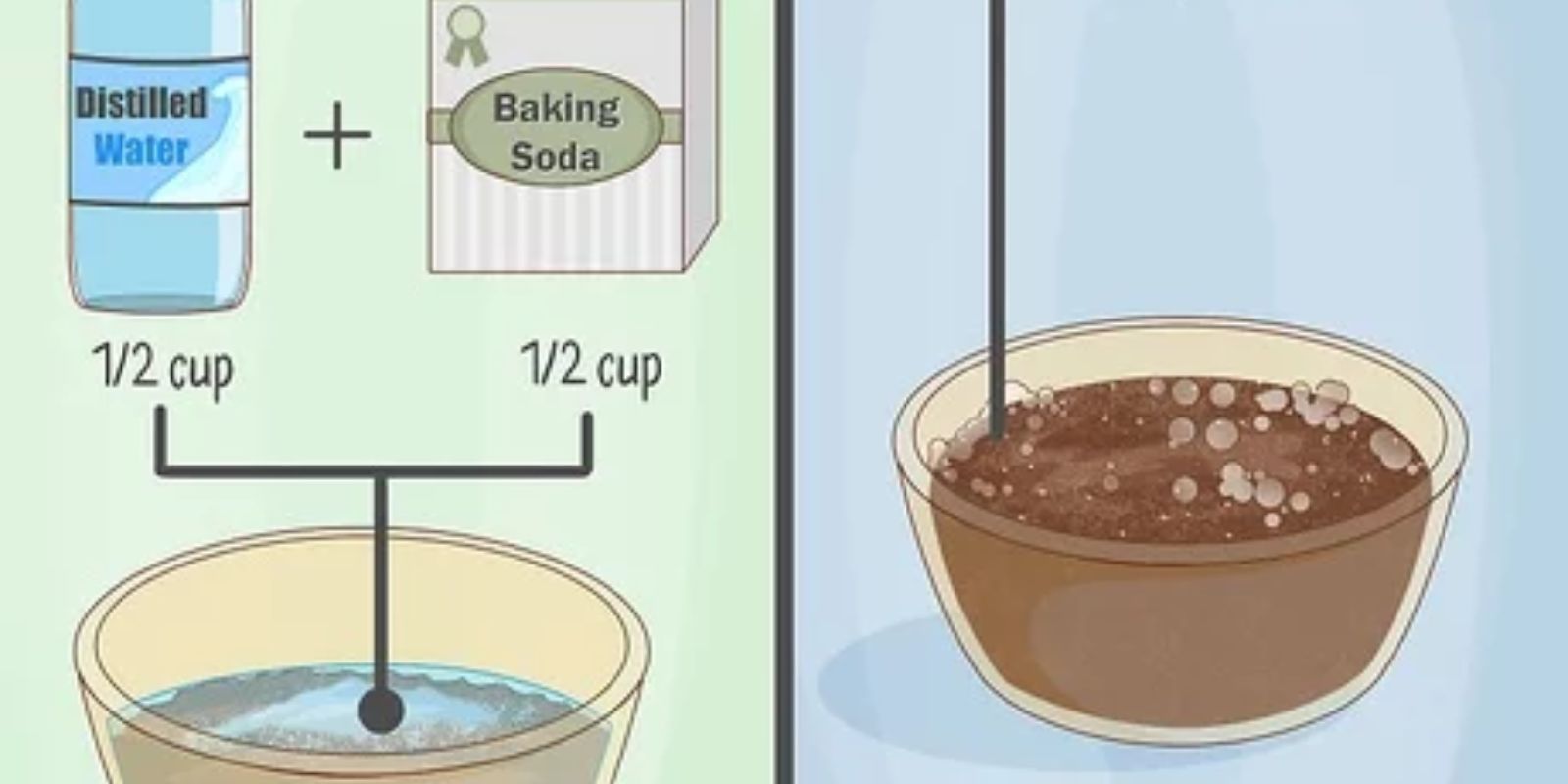
Option 2: DIY Vinegar and Baking Soda Test
- Take two small soil samples.
- In one sample, pour vinegar. If it fizzes, your soil is alkaline (above 7.0).
- In the other sample, add water and then a bit of baking soda. If it fizzes, your soil is acidic (below 7.0).
- No fizzing means your soil is likely neutral.
3. Check Soil Drainage
To test how well your soil drains:
- Dig a hole about 12 inches deep.
- Fill the hole with water and let it drain completely.
- Refill the hole and observe how long it takes to drain the second time.
- Good drainage: Water drains within 30 minutes to 1 hour.
- Poor drainage: Water takes longer than 1-2 hours to drain, which may indicate clay soil or compacted areas.
- Fast drainage: Water drains in less than 30 minutes, which may suggest sandy soil.
4. Assess Soil Texture
Determining the texture of your soil can help you understand how well it holds water and nutrients:
The Jar Test:
- Fill a clear jar halfway with soil.
- Add water to the top and shake vigorously.
- Let the jar sit for a few hours.
- The soil will settle into layers: sand at the bottom, silt in the middle, and clay on top.
- The relative thickness of each layer tells you the soil texture.
- If you have mostly sand, your soil drains fast but may lack nutrients.
- If the majority is clay, the soil may hold water but could become compacted.
- Loamy soil will have a balanced mixture of all three.
5. Test Nutrient Levels
At-home soil test kits can provide a basic understanding of your soil’s nutrient content, especially the levels of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). Here’s how you can test it:
- Purchase a nutrient test kit from a garden center.
- Follow the instructions to take soil samples, mix them with the provided solution, and observe the color change.
- Compare the results with the provided chart to determine if your soil is deficient in key nutrients.
Alternatively, you can send a soil sample to a local agricultural extension service for more detailed nutrient analysis.
6. Improve Your Soil Based on Results
Once you’ve tested your soil and have the results, you can make adjustments:
- If your soil is too acidic (low pH): Add lime to raise the pH.
- If your soil is too alkaline (high pH): Add sulfur or organic matter to lower the pH.
- If your soil lacks nutrients: Add compost, manure, or balanced fertilizers depending on what nutrients are lacking.
- If your soil has poor drainage: Consider amending it with organic matter like compost, peat moss, or perlite.
- If your soil texture is sandy or clay-heavy: Incorporate organic matter to improve water retention or drainage.
7. Consider Adding Organic Matter
No matter what your soil test results are, adding organic matter (like compost or well-rotted manure) is one of the best ways to improve soil health. Organic matter helps with water retention, aeration, and nutrient availability, making it an essential component of healthy soil.
Conclusion
Testing your soil is an easy, yet highly beneficial task that helps you understand its pH, nutrient levels, drainage capacity, and texture. This knowledge allows you to make precise adjustments, ensuring that your plants get exactly what they need to thrive. Healthy soil is key to a flourishing garden, and the steps outlined above provide a practical, at-home way to unlock your soil’s potential.
Motivation Sentence:
Now it’s your turn! Get started with soil testing today and see how your garden can flourish! 🌱💧
#SoilTesting #HealthySoil #GardeningHacks #GardenLife #HomeGardening #GreenThumb #PlantCare #OrganicGardening