Bamboo, known for its fast growth and serene, green beauty, is a popular plant for both ornamental and practical purposes in gardens. Its rapid growth rate and distinctive aesthetic make it a favorite for creating privacy screens, adding a touch of elegance to landscapes, and even as a renewable resource. But buying bamboo plants can be expensive, especially if you want a lush, dense garden. Fortunately, bamboo is one of the easiest plants to propagate, and with just a few simple techniques, you can multiply your bamboo plants at home.
In this guide, we’ll explore three effective methods for propagating bamboo: by division, using rhizomes, and through cuttings. Each method offers unique benefits and challenges, allowing you to choose the one that suits your experience level, available materials, and the type of bamboo you’re growing.
Why Propagate Bamboo?
Before diving into the methods, it’s helpful to understand why you might want to propagate bamboo:
- Save Money: Buying bamboo plants can be costly, but propagation allows you to grow new plants for free.
- Expand Your Garden: With a few starter plants, you can easily create a dense bamboo grove over time.
- Share with Others: Propagating bamboo lets you share this beautiful plant with friends and family.
- Sustainable Gardening: Bamboo is eco-friendly and renewable, and propagating your plants contributes to a greener environment.
Ready to create your own bamboo haven? Let’s break down the three methods to get you started.
Method 1: Propagation by Division
The division method is one of the most effective ways to propagate bamboo and is ideal for clumping types of bamboo.
Steps to Propagate Bamboo by Division:
- Choose a Healthy Bamboo Clump: Select a mature bamboo plant with several healthy culms (stems) and a well-developed root system.
- Dig Up the Clump: Using a sharp spade, dig around the base of the bamboo clump. Be sure to dig wide and deep enough to capture an entire section of roots and shoots.
- Separate the Section: Carefully separate a clump containing several culms, ensuring that each section has roots and at least one healthy shoot. If the clump is large, use a saw to divide it.
- Replant the Division: Plant the division in a new location, digging a hole large enough for the root ball. Cover with soil, press firmly, and water thoroughly.
- Maintain Moisture: Water the newly planted division regularly for the first few weeks to help it establish in its new location.
Tips for Success:
- Time of Year: Spring or early summer is ideal for bamboo division as the plant is actively growing, and the warmer temperatures promote faster recovery.
- Prepare Soil: Ensure the planting site has nutrient-rich, well-draining soil to support healthy root development.
Method 2: Propagation from Rhizomes
Bamboo rhizomes, or underground stems, are the primary way that bamboo spreads naturally. This method works best with running bamboo varieties, which naturally produce long, spreading rhizomes.
Steps to Propagate Bamboo from Rhizomes:
- Locate the Rhizomes: Dig around the base of the bamboo plant to expose the rhizomes. These will appear as thick, root-like structures that grow horizontally underground.
- Select Healthy Rhizomes: Choose a rhizome that has at least one or two healthy nodes and buds, which will eventually produce new shoots.
- Cut and Prepare the Rhizome: Cut a section of rhizome about 12-18 inches long, ensuring that it includes a bud or node, as this is where new growth will emerge.
- Plant the Rhizome: Dig a shallow trench and lay the rhizome horizontally in the soil. Cover it lightly with soil, leaving any buds near the surface.
- Water Regularly: Water the rhizome thoroughly after planting and keep the soil moist, but avoid overwatering.
Tips for Success:
- Timing: Late winter to early spring is ideal for rhizome propagation, as this allows the rhizome to grow as temperatures rise.
- Patience: Rhizome propagation may take several weeks before you see new growth, so be patient and keep the soil consistently moist.
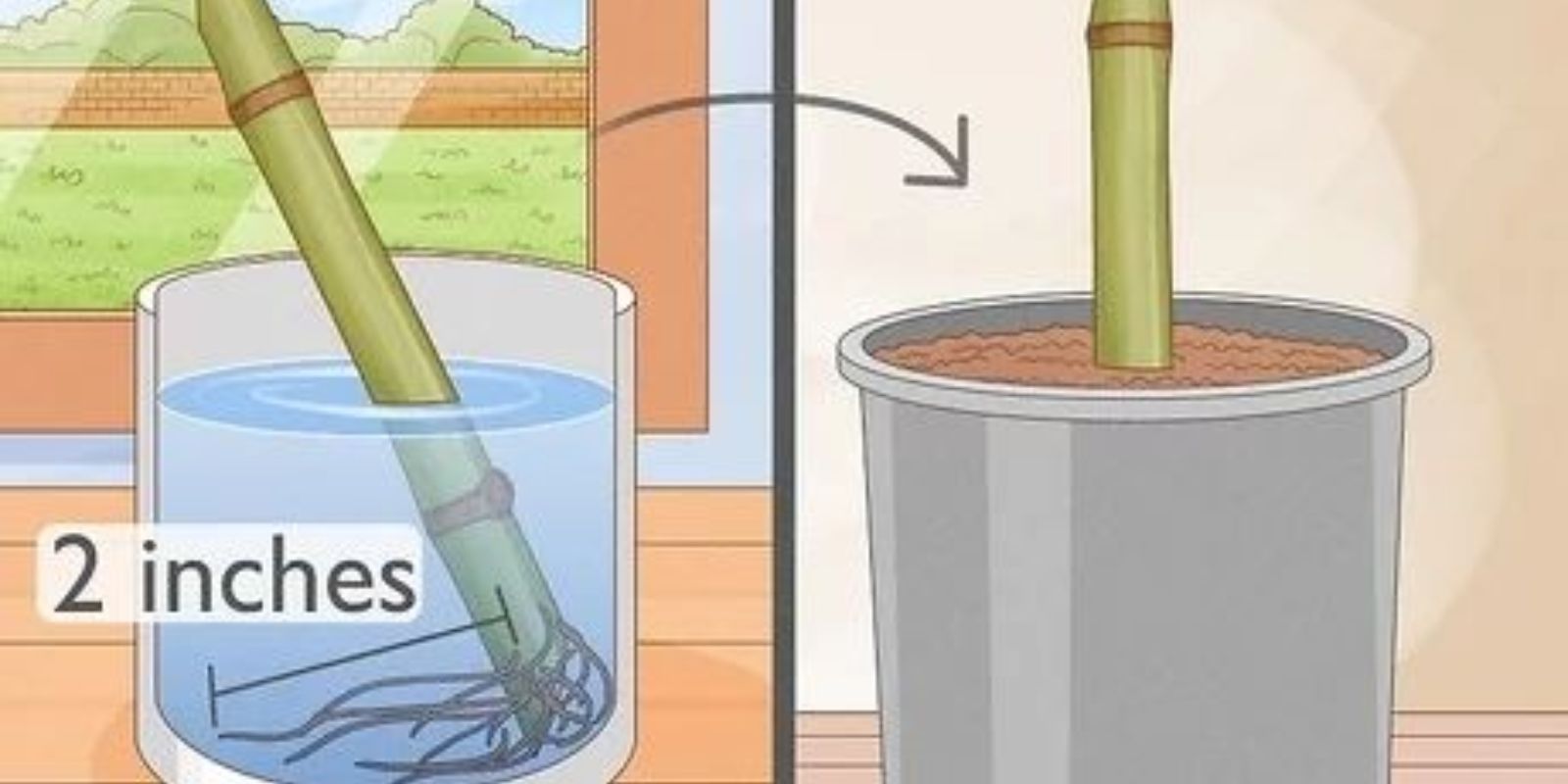
Method 3: Propagation by Cuttings
Bamboo can also be propagated by cuttings, though this method is typically less successful and requires careful handling. It works best with smaller, shrubby varieties of bamboo.
Steps to Propagate Bamboo from Cuttings:
- Select a Healthy Culm: Choose a young, healthy bamboo stem that has a diameter of about 0.5 to 1 inch and several nodes.
- Prepare the Cutting: Cut the bamboo culm just above a node at the top and below a node at the bottom. Each cutting should be 12-18 inches long and have 2-3 nodes.
- Place in Water or Soil: You can either place the cutting in a container of water or plant it directly in soil. If using water, make sure to keep the water level just below the nodes. If planting in soil, bury the cutting up to the first node.
- Provide Proper Conditions: Keep the cutting in a warm, humid environment and away from direct sunlight. If in soil, ensure the soil is moist but well-draining.
- Wait for Roots to Develop: In a few weeks, roots should begin to form. When roots are well-established, you can transplant the cutting to a larger pot or directly into the garden.
Tips for Success:
- Humidity: Bamboo cuttings thrive in high humidity, so mist regularly or place a plastic cover over the cutting to retain moisture.
- Use Rooting Hormone: Applying rooting hormone to the base of the cutting can increase the chances of successful root development.
Additional Tips for Propagating Bamboo
Regardless of the propagation method you choose, here are a few tips to improve your success rate:
- Choose the Right Bamboo Type: Different bamboo species respond better to different propagation methods. Clumping bamboo is ideal for division, while running bamboo is well-suited for rhizome propagation.
- Provide Adequate Space: Bamboo spreads quickly, so if you’re planting directly in the ground, make sure it has enough room. Consider installing a barrier for running bamboo to prevent it from spreading uncontrollably.
- Water Consistently: Newly propagated bamboo needs regular watering to establish itself. Avoid waterlogging but ensure the soil remains moist.
- Avoid Direct Sunlight: Young bamboo plants can be sensitive to direct sunlight. Keep them in indirect light or partial shade until they are strong enough to withstand full sun exposure.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- No New Growth: If your propagated bamboo isn’t showing new growth, check for adequate moisture, temperature, and light. Bamboo needs consistent care, especially in its early stages.
- Yellowing Leaves: This could be a sign of too much sunlight or a nutrient deficiency. Adjust the plant’s light exposure or consider adding a balanced fertilizer.
- Wilting or Drooping: Overwatering or underwatering can cause wilting. Ensure that your soil is well-draining and water according to the plant’s needs.
Benefits of Growing Bamboo in Your Garden
- Natural Privacy: Bamboo’s tall, dense growth makes it an ideal natural screen.
- Sustainable Resource: Bamboo is highly renewable and has a low environmental impact, making it a great sustainable choice.
- Low Maintenance: Once established, bamboo is relatively low maintenance, requiring minimal pruning and care.
- Versatile Use: Bamboo can serve as a decorative element, a windbreak, or even a sustainable resource for small DIY projects.
Conclusion
Propagating bamboo is a rewarding project that allows you to create more plants without the expense of purchasing new ones. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced gardener, the methods of division, rhizome propagation, and cuttings each offer unique advantages. With a little patience and proper care, you can cultivate a lush bamboo grove in your garden, enjoying the beauty and versatility that bamboo brings.
Are you ready to expand your bamboo garden? Share your propagation journey and connect with fellow plant enthusiasts! 🌱 #BambooPropagation #GreenThumb #GardenTips #EcoFriendlyGardening #BambooLove #PlantPropagation