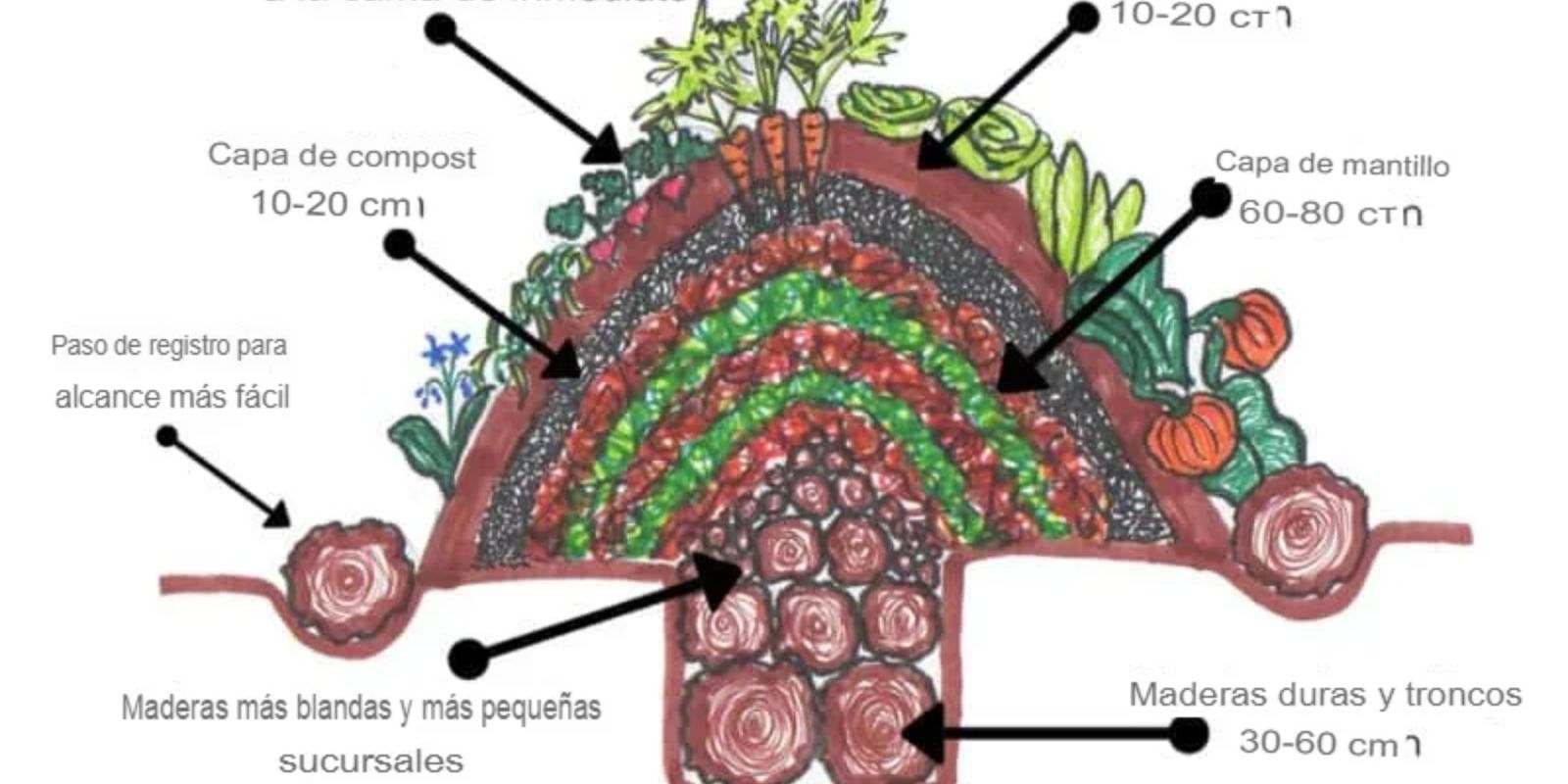
Introduction
Gardening on a slope or uneven terrain can be a challenge, but it doesn’t have to be. One effective way to transform these areas into productive garden spaces is by creating steep raised garden beds, or “bancales empinados y escarpados.” This gardening method maximizes your space while improving drainage and accessibility, making it easier to tend to your plants. Whether you’re working with a small garden or have a larger area to improve, steep raised beds offer a solution that is both functional and aesthetically pleasing. In this article, we will explore the benefits of steep raised beds and provide a detailed, step-by-step guide on how to create them in your own garden.
Why Choose Steep Raised Beds?
Raised beds are a popular gardening technique due to their numerous advantages. By elevating the soil, raised beds allow for better control over soil quality, reduce soil compaction, and provide improved drainage. But when working with a sloped garden, raised beds become even more beneficial. Here’s why:
- Maximized Space: Raised beds help to fully utilize the available space, especially when working with sloped or hilly terrain. You can turn a challenging slope into a productive growing area.
- Better Drainage: Sloped beds allow excess water to flow away naturally, preventing waterlogging, which is common in traditional flat garden beds.
- Ease of Access: Steep raised beds make it easier to reach plants without having to bend over too much, making gardening more comfortable, especially for those with back issues.
- Improved Soil Control: You can add high-quality soil to a raised bed, ensuring that your plants grow in the best possible conditions.
Creating a sloped raised garden bed can be a rewarding project that enhances both the aesthetic and practical aspects of your garden. Let’s break down the process step by step.
Step 1: Choose the Right Location
Before you start building your raised beds, it’s essential to select the right location. Look for a sloped area that receives adequate sunlight throughout the day. Most vegetables and flowers need at least six hours of direct sunlight, so try to find a spot that meets these requirements. Keep in mind the following factors:
- Sunlight: Select a spot with good exposure to sunlight. While some plants can tolerate partial shade, the majority of garden plants thrive in full sun.
- Water Flow: Check the water flow in the area. Slopes can sometimes lead to water runoff, so ensure that the slope isn’t too steep, and there’s no risk of erosion.
- Accessibility: Make sure the site is accessible for maintenance and harvesting. Consider how easy it will be to reach and care for your plants once the beds are built.
Step 2: Mark the Area
Once you’ve chosen the ideal location, it’s time to mark out the boundaries of your raised bed. This step will help you visualize the space and determine the size and shape of the bed.
- Use stakes and string to outline the shape of the bed. The layout doesn’t have to be square or rectangular – you can make the bed any shape that fits your garden’s layout.
- Measure the slope’s angle to determine how steep you want the bed to be. A moderate slope (10-15 degrees) is ideal for easy access and water drainage, while too steep of an incline could make it difficult to maintain.
- Ensure that the length of the bed is comfortable for working. Typically, raised beds should not be wider than 4 feet, so you can easily reach across from both sides.
Step 3: Build the Base
The base of your steep raised bed will play a crucial role in stabilizing the structure. The goal is to ensure that the bed doesn’t slide or shift over time, especially with the added weight of soil. Here’s how you can build a sturdy base:
- Level the bottom of the slope: If the slope is particularly steep, you may need to level off part of the ground where the base will sit. This can be done by digging into the slope, or in some cases, building retaining walls to prevent soil movement.
- Add gravel or crushed stone: To help with drainage, add a layer of gravel or crushed stone at the base of the bed. This will allow water to drain through the soil and prevent root rot.
- Use edging materials: Select durable materials for the edging of your bed, such as stone, wood, or concrete blocks. These materials will hold the bed’s shape and keep the soil in place.
Step 4: Create the Walls
Building the walls of the raised bed is a crucial step in ensuring that your bed is strong and will last for years. The walls need to be sturdy enough to support the soil and withstand weather conditions like wind and rain.
- Choose your materials: Common materials for creating raised bed walls include wood (cedar or redwood), brick, stone, or concrete blocks. Each material has its advantages, so choose one that fits both your aesthetic preferences and your budget.
- Stacking the walls: If using wood or stone, you will need to stack the materials in layers. Make sure the materials are secure and level as you go. For wooden beds, screws or nails are typically used to fasten the boards together. For stone, use mortar or stacking techniques.
- Height of the walls: The walls should be at least 18-24 inches tall to give the plants enough room to grow. If you want deeper beds, you can stack additional layers for taller sides.
Step 5: Fill the Raised Bed with Soil
Now comes the fun part: filling your raised bed with soil! The quality of the soil you choose is essential for healthy plant growth, so opt for a good mix of nutrient-rich soil, compost, and organic matter.
- Soil mixture: A typical mix for raised beds includes 60% topsoil, 30% compost, and 10% soil amendments like peat moss, perlite, or vermiculite. This blend will provide your plants with the necessary nutrients and improve drainage.
- Layering: Begin by adding soil to the bottom of the bed and work your way up. Ensure that the soil is evenly spread and compacted gently, but avoid packing it down too hard, as this can restrict root growth.
- Level the soil: After filling the bed, use a rake to level the surface of the soil. This will help ensure even growth for all of your plants.
Step 6: Plant and Maintain Your Raised Bed
With your steep raised bed in place and filled with soil, it’s time to start planting. Choose plants that thrive in raised beds and take advantage of the improved drainage and nutrient-rich soil. Here are a few tips for planting and maintaining your steep raised bed:
- Plant spacing: Ensure that you plant your vegetables or flowers with enough space to grow. Pay attention to their height and spread to avoid overcrowding.
- Watering: Raised beds tend to dry out faster than ground-level beds, so make sure to water regularly. Consider setting up an irrigation system for easy watering, especially during hot weather.
- Mulching: To retain moisture and suppress weeds, add a layer of mulch on top of the soil. Organic mulches like straw, wood chips, or leaves work well for this purpose.
- Regular maintenance: Keep the bed free of weeds, and check for any pests or diseases regularly. Make sure to harvest your crops when they’re ready to prevent overcrowding.
Conclusion
Creating steep raised garden beds is an excellent way to transform sloped areas into productive and efficient garden spaces. With the right planning and materials, you can build a structure that not only looks great but also enhances your garden’s productivity. The benefits of steep raised beds—better drainage, improved accessibility, and maximized space—make them a smart investment for any gardener, regardless of experience level.
So, why wait? Start planning your steep raised beds today and take your gardening to new heights!
Motivational Sentence
“Transform your garden and watch your plants flourish by creating efficient, sloped raised beds. It’s time to maximize your space and gardening potential!”